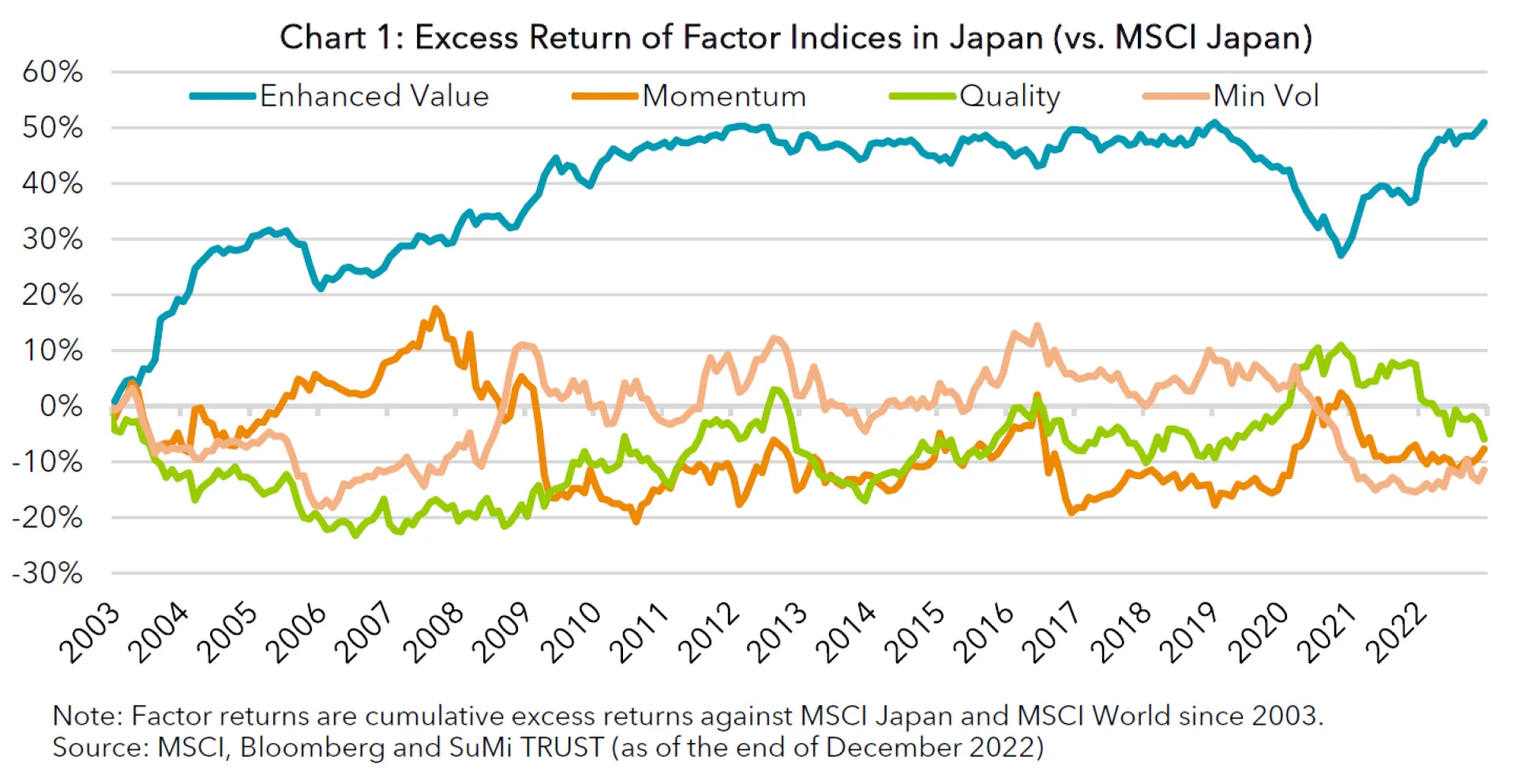
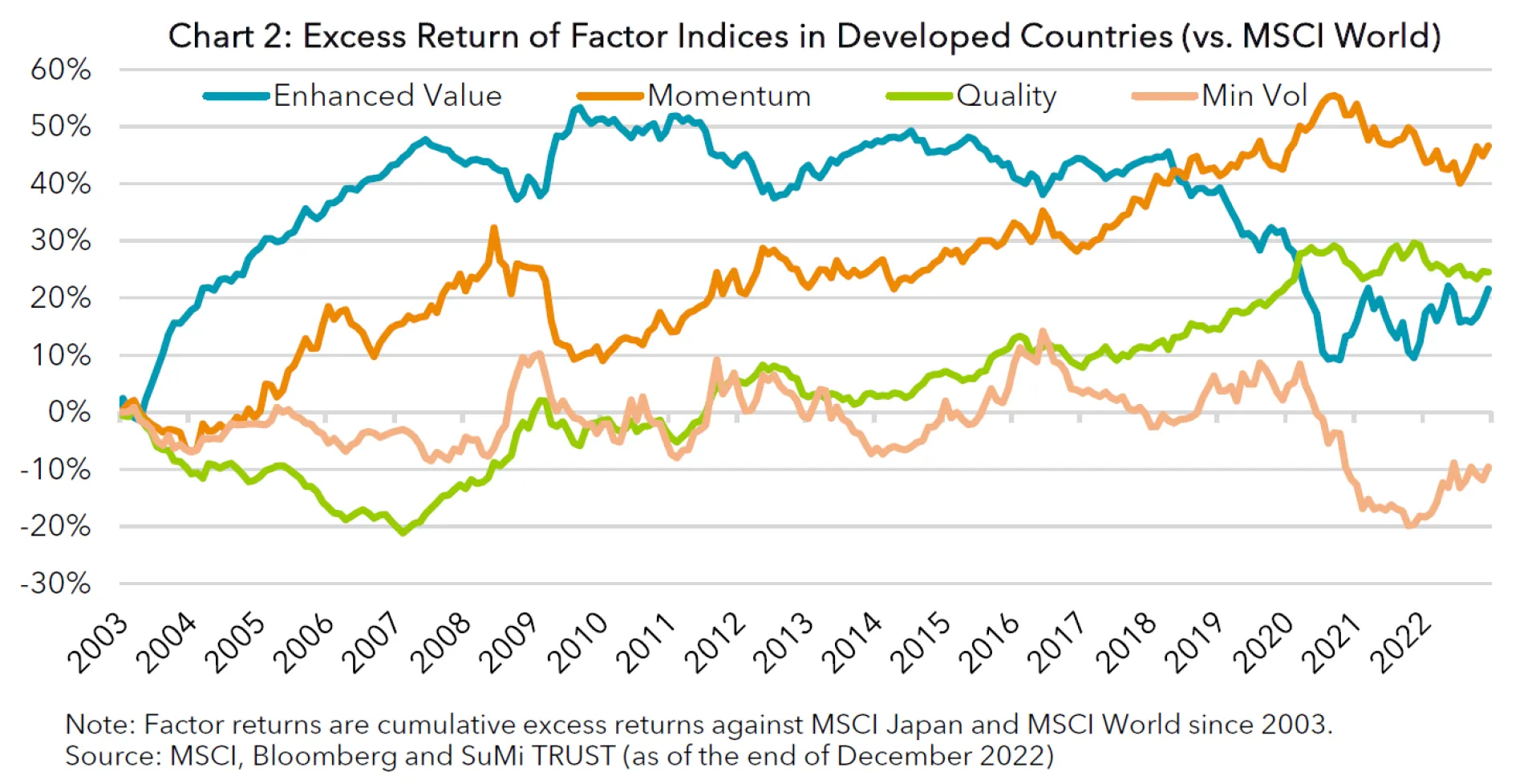
1. Factors behave differently in markets
The charts above show excess returns generated by four MSCI factor indices - Value, Momentum, Quality and Minimum Volatility factors - constructed upon MSCI’s traditional market cap weighted indices in developed countries and the Japanese market. As you can see, these charts are quite different. Whilst three out of the four global factors have outperformed their parent index, only one of the four Japanese factor indices posted higher returns than the market-cap weighted index. When you compare individual factors, Value factors have been effective and Minimum Volatility factors have slightly underperformed their parent indices in both markets. Momentum and Quality factors have shown significantly different results in the two markets, posting positive alpha in the developed markets and generating lower-than-the-market returns in Japan. This is consistent with what is widely believed; Momentum and Quality factors do not work well in Japan. Some may insist that efficacy of the Momentum factor should be evaluated in combination with the Value factor. In Japan, the Momentum factor was highly effective when analysing Value and Momentum factors together*2.
However, we believe it is worthwhile to scrutinise 1) whether or not Momentum and Quality factors generate outperformance in Japan and 2) whether localisation is useful to capture a “factor premium” in the country. As we will see in the following sections, our experience suggests that both Momentum and Quality factors are actually effective in the Japanese market as individual factors and this indicates that factor premium in Japan cannot be well captured by global factor indices.
*2 Cliff Asness (2011) “Momentum in Japan: The Exception that Proves the Rule” Asness argued that Value and Momentum factors should be studied as a system and showed that the Momentum factor was actually successful in Japan when it was viewed as a system with the Value factor
2. Building Effective Momentum Factor in Japan
Momentum factor investments aim to take exposure to high momentum stocks. A Momentum factor index generally consists of the best performing stocks in the recent past. Existence of the Momentum risk premium, which refers to the phenomenon in which prices that increased in the prior period tend to keep increasing in the following period, is confirmed in the global market by a wide range of academic research. Academic research also suggests that the Momentum factor is not effective in Japan. In fact, the chart above shows that MSCI’s Momentum factor index has failed to outperform the market in Japan for the last 20 years.
In order to examine if the Momentum risk premium exists in Japan, we began by looking at underlying drivers behind the Momentum risk premium. An academic study conducted by Novy-Marx*3 revealed that the Momentum risk premium comes from earnings momentum. This indicates that price momentum is just a proxy which actually captures earnings momentum. In other words, the Momentum risk premium is not a technical anomaly, but it is brought on by investing in companies which achieved, and are likely to continue, positive earnings growth. When we conducted the same analysis for the Japanese market, the result indicated that earnings momentum is effective to predict future stock prices in Japan as well. Although the Momentum risk premium may not be captured in Japan by focusing on price momentum, it could be captured by focusing on earnings momentum itself.
*3 Robert Novy-Marx (2017) ”Fundamentally, Momentum Is Fundamental Momentum”, Journal of Portfolio Management
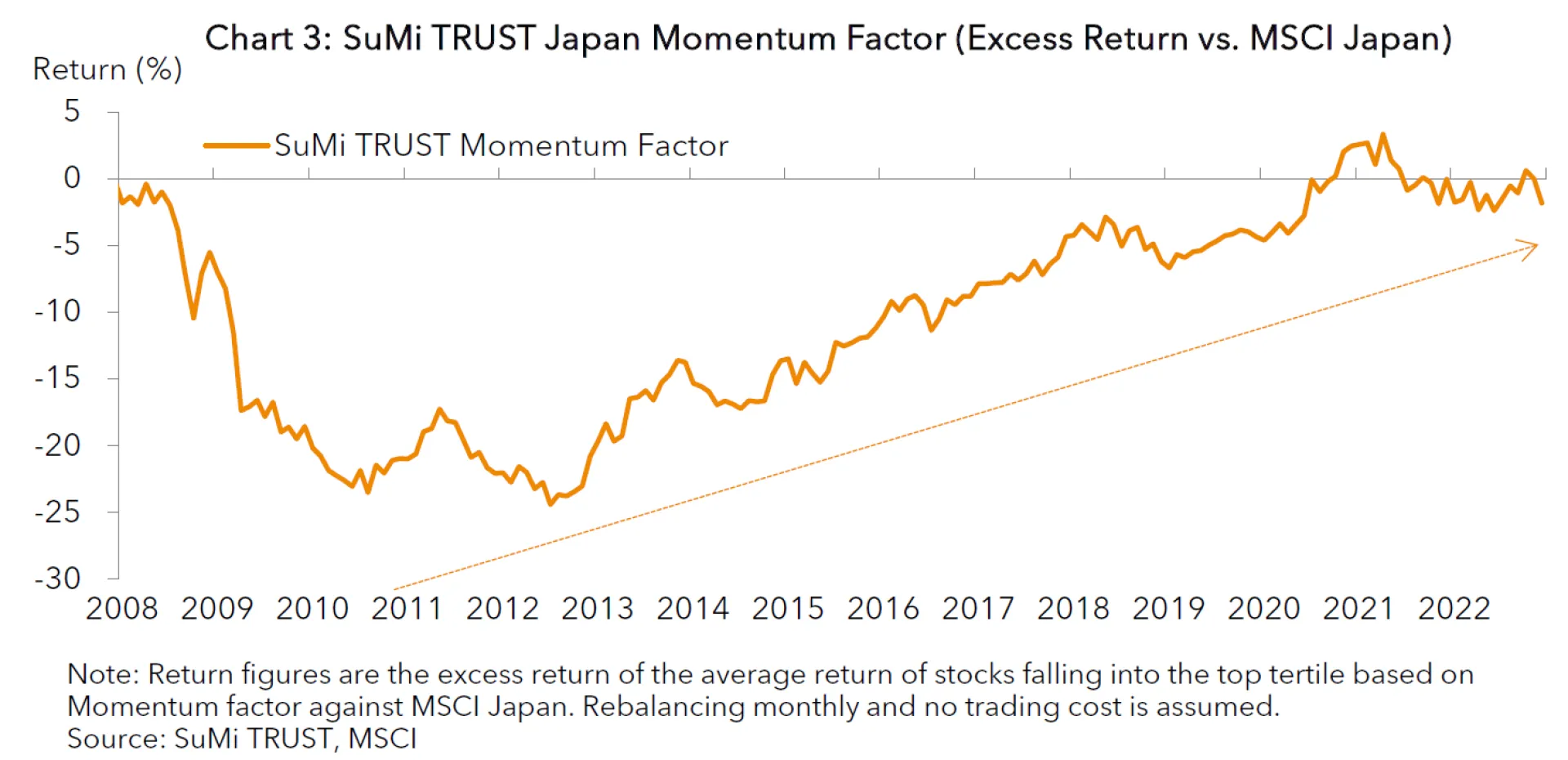
Based on the finding that the Momentum risk premium exists and can be captured in Japan, we have designed our proprietary Momentum factor for the Japanese market. Given the fact that the most investors use a multi-factor approach in the factor investments field, we designed a simple factor by just featuring earnings momentum*4. As shown in Chart 3, this Momentum factor strategy has steadily outperformed the market cap index except from mid-2008 to mid-2010, mostly during the Global Financial Crisis (GFC) in 2008 and 2009.
*4 We use Price Momentum in addition to Earnings Momentum for Momentum factor investments that is offered as a standalone strategy. For a multi-factor strategy, we focus on Earnings Momentum aiming to lower the turnover ratio.
3. Building Effective Quality Factor in Japan
The Quality risk premium exists as higher quality companies tend to generate better performance than lower quality companies. Whilst the Quality factor is one of the most widely used factors, there are various definitions of Quality. One may say Quality is sound financial conditions and others may say it is earnings quality, which is often measured by using accruals as a proxy variable, the amount of earnings that the management of company can manipulate. Profitability and earnings stability are also commonly used definitions as well as low investment*5.
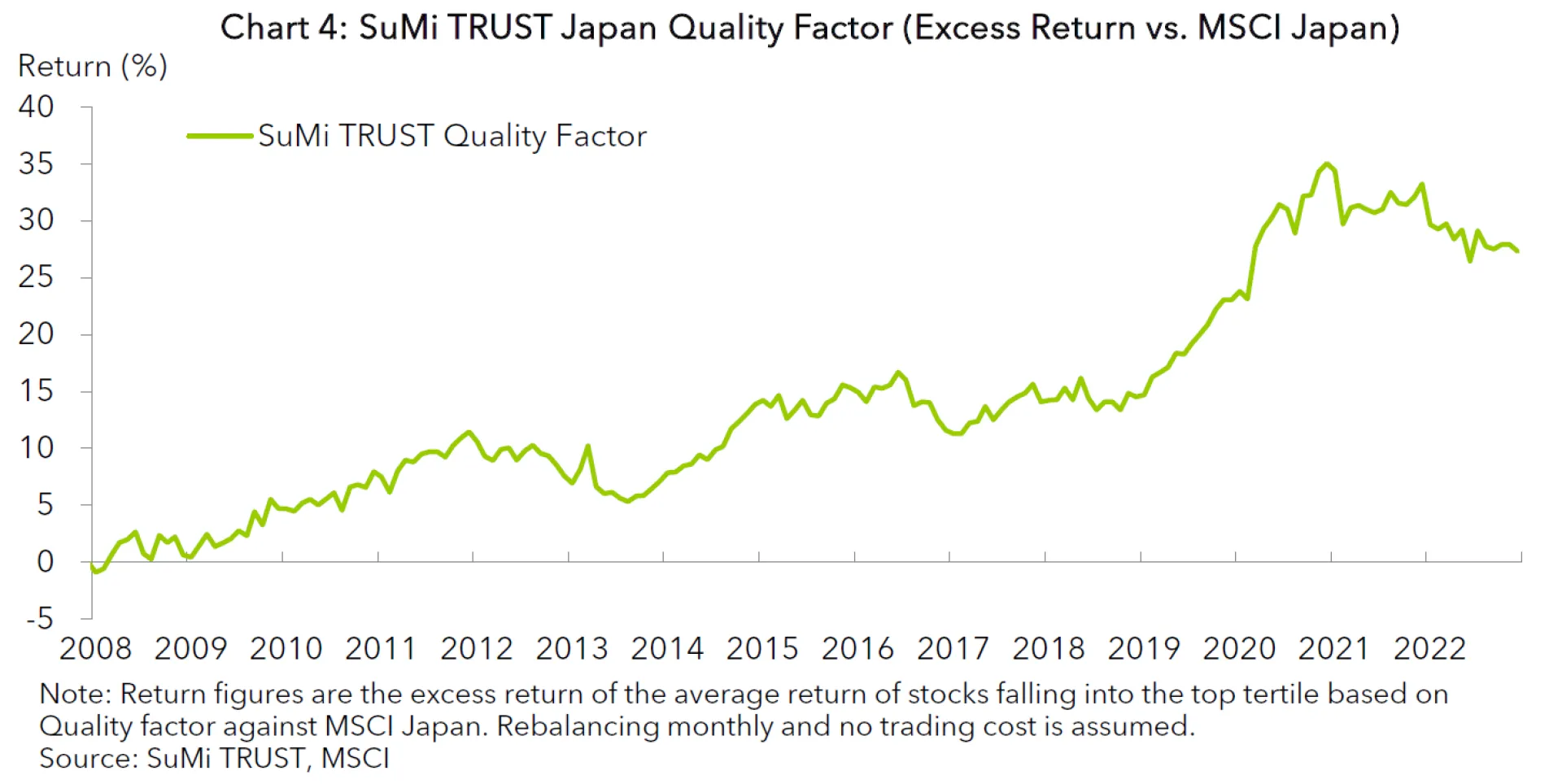
At SuMi TRUST, we define the Quality factor as a company’s ability to generate strong earnings and a solid balance sheet. We use profitability as a primary factor. Fama and French, in their 2006 paper*6, employed ROE as a profitability factor. Novy-Marx showed that Gross Profitability on Assets (GPA) is a more effective indicator to explain future returns than ROE*7. We have compared effectiveness of ROE and GPA as profitability factors in the Japanese market and found that GPA is more effective than ROE in Japan as well. Furthermore, GPA has an advantage over ROE as a Quality indicator as it is not affected by the capital structure of a company. A company is able to improve ROE by increasing leverage (e.g. share buybacks or dividend), but this is not possible for GPA. We have decided to use GPA as the main input for our Quality factor strategy based on this result.
In addition, we also employ Sales Stability and Low Leverage as secondary inputs. We understand earnings stability is more commonly used than sales stability in Quality factors. Why we prefer Sales Stability over Earnings Stability is that the former is less affected by the company management than the latter and, therefore, better reflects the actual stability of a business than Earnings Stability. The Chart 4 above shows the performance of the SuMi TRUST Quality Factor strategy, which consists of GPA, Sales Stability and Low Leverage. The strategy has steadily outperformed the market cap index.
*5 MSCI designs its Quality index from Return on Equity (ROE), Debt to Equity and Earnings Variability. i.e. the index comprises of profitability, low leverage and earnings stability. FTSE use profitability, efficiency, earnings quality and leverage.
*6 Fama and French (2006) “Profitability, investment and average returns”, Journal of Financial Economics Fama and French suggested that stock returns can be explained by Price-to-Book, Profitability and Low Investment.
*7 Novy-Marx (2013) “The other side of value: The gross profitability premium” , Journal of Financial Economics
4. Diversification Benefit and Return from Multi-Factor Strategy
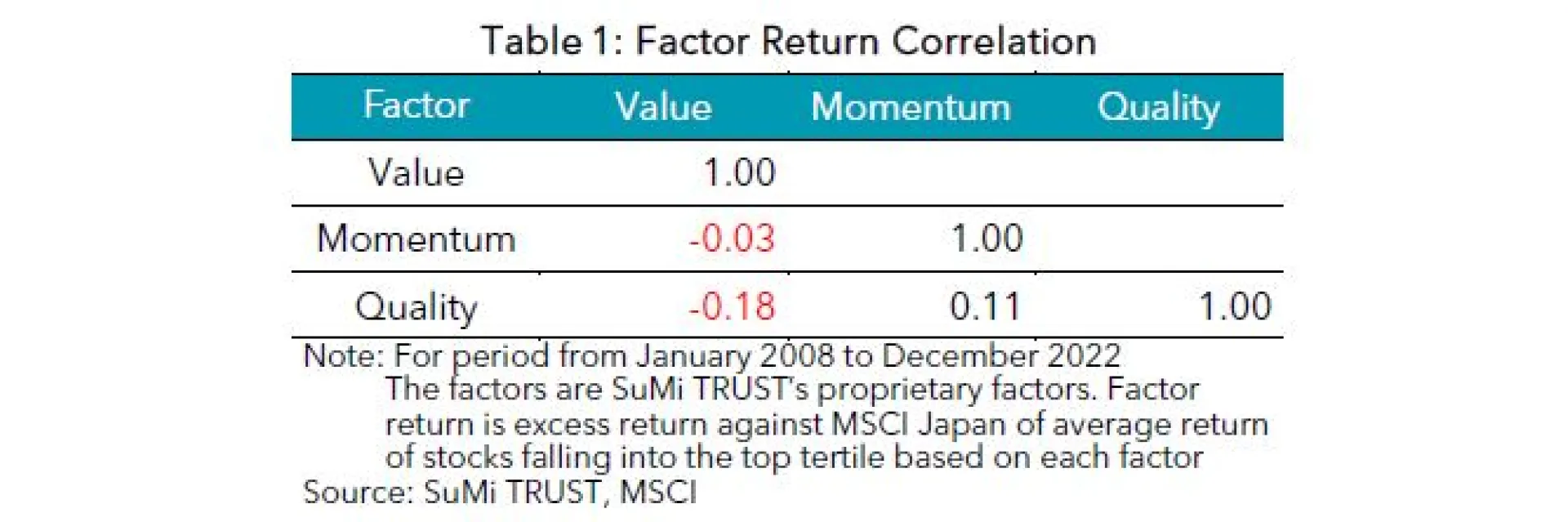
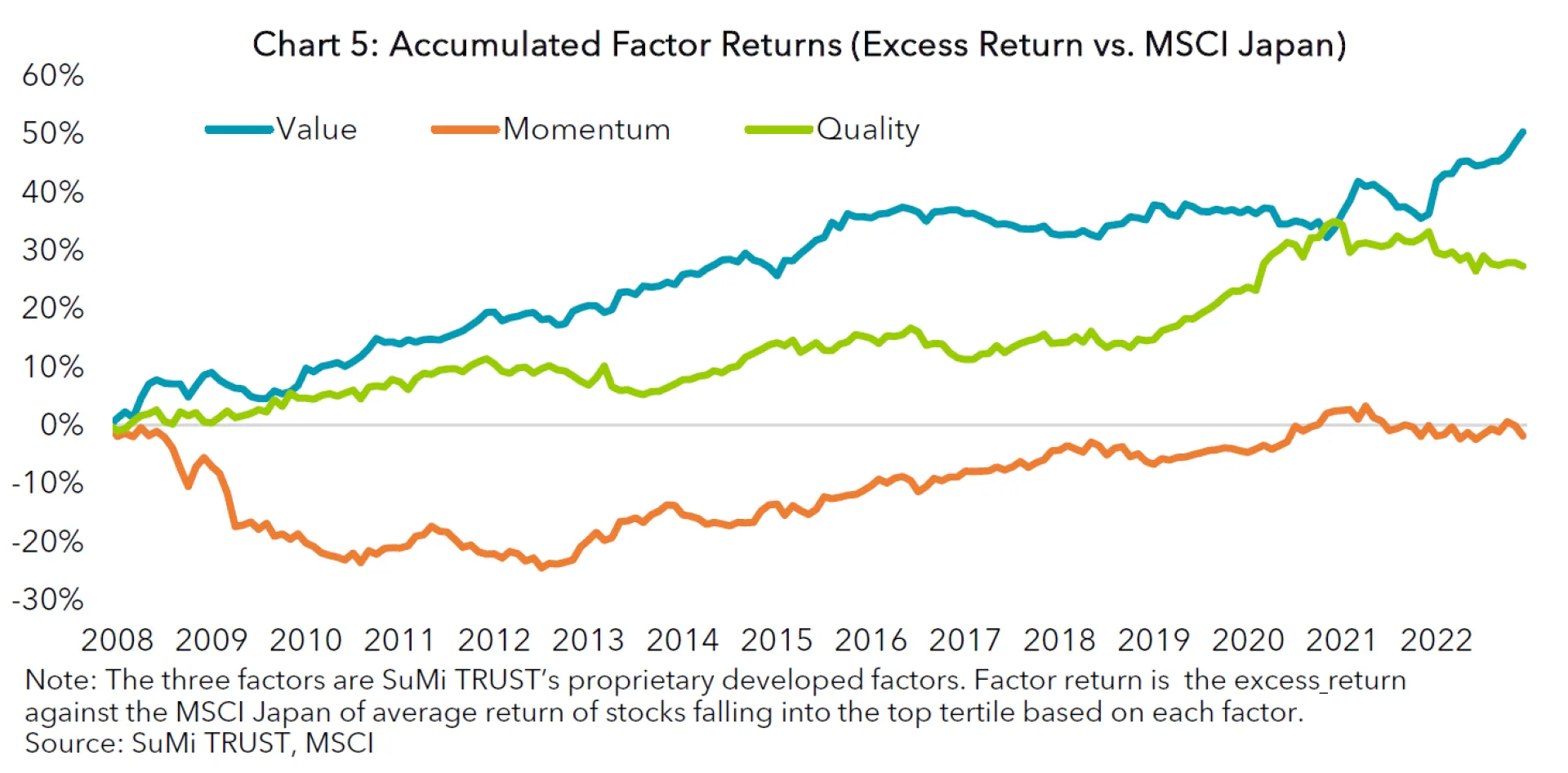
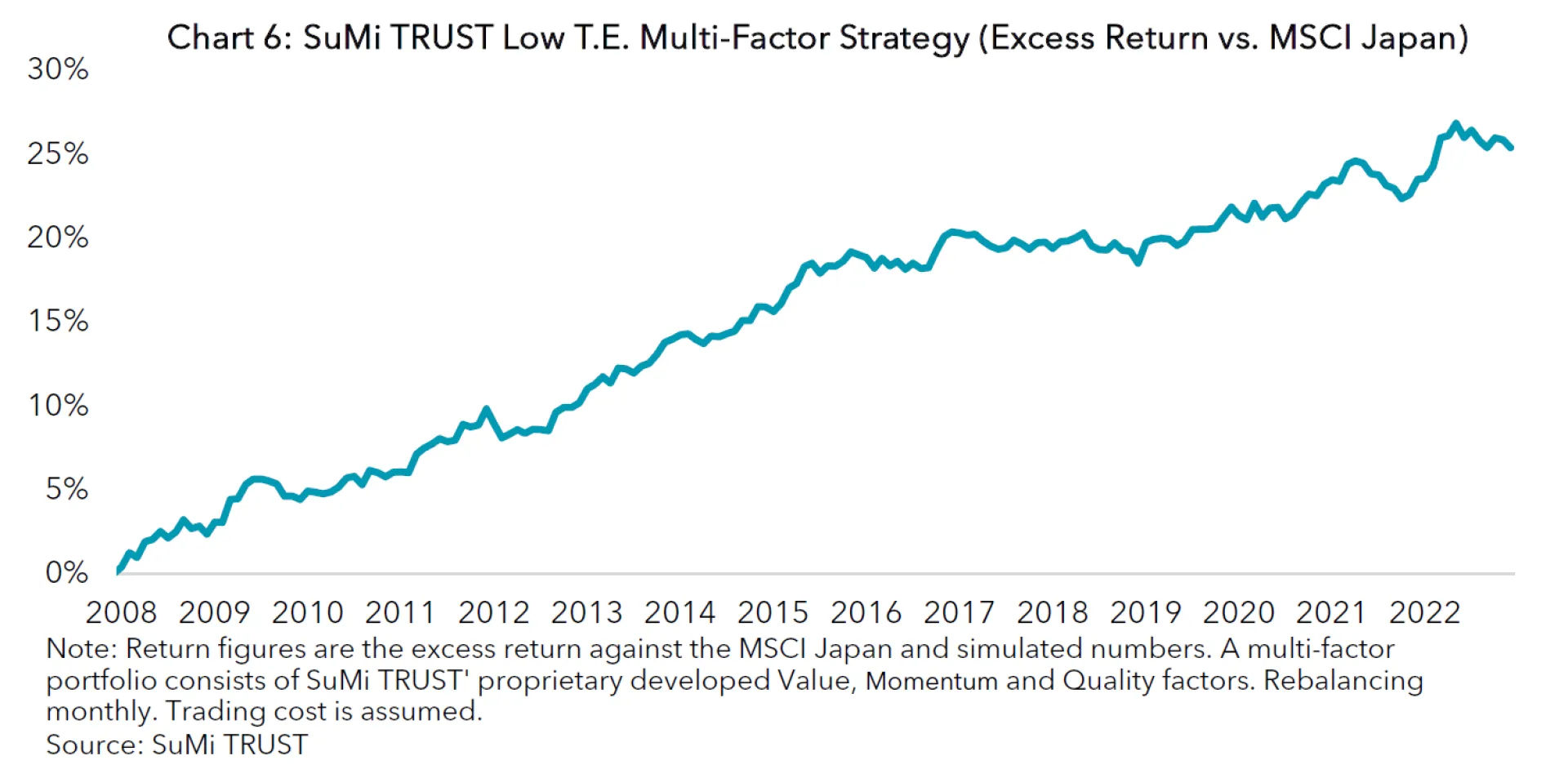
Although factor indices are believed to deliver excess returns against their parent index in the long-run, it is typical for them to have a multi-year period of underperformance as well as outperformance. This characteristic lets a majority of investors employ a multi-factor approach. With a multi-factor strategy in mind, a factor index is assessed not only by its outperformance against its parent index, but also by its correlation versus other factor indices. For a multi-factor long only portfolio, we typically blend three factor strategies, namely Value, Momentum and Quality factors. Our proprietary factors have virtually no correlation among each other (see Table 1). When combined, the three factors complement each other (see Chart 5) and our Low T.E. Multi-Factor Portfolio, which consists of the three, generated consistent returns (see Chart 6). During the GFC, the Momentum factor experienced a severe drawdown whilst the Value and Quality factors outperformed the market. When the Value factor failed to generate excess returns for some years until 2021, the Momentum and Quality factors offset this by generating alpha. In 2021 and 2022, when the Momentum and Quality struggled amid strong value reversal, the Value factor achieved strong outperformance.
5. Summary
The recent strong value stock recovery following a multi-year rally of quality/growth stocks seems to attract institutional investors’ attention to factor investments. When investors allocate to factor investing, they expect the factor portfolio to increase returns and reduce costs in addition to benefit of optimising risks. In this regard, a factor strategy is viewed as a lower cost alternative to traditional active strategies. When it comes to a traditional active strategies, investors often hire regional managers expecting their local specialties. However, it is typical for the same investors investing in factor strategies through global mandates. As shown in this paper, we are convinced that one global factor does not always fit all regions and regional factor strategies have the potential to outweigh global ones. The analysis introduced in this paper shows that localised factor strategies have generated better performance than global indices in Japan and therefore investors could benefit from strategies developed by a local specialist.

